다양한 분야에서 혁신적인 솔루션을 지원합니다.
제품 설명
Factor B (complement fragment Bb) ELISA Kit
제품 번호
DEIASL036
제품 특징
Factor B (Complement Fragment Bb) ELISA Kit for Pathological Research
이 유전자는 보체 인자 B를 인코딩하며, 이는 보체 활성화의 대체 경로에 속하는 구성 요소입니다. 보체 인자 B는 혈액에서 단일 체인 폴리펩타이드 형태로 순환하며, 경로가 활성화되면 보체 인자 D에 의해 절단되어 비촉매 체인 Ba와 촉매 소단위 Bb를 생성합니다 (NIH). 대체 보체 경로는 특이적인 항체가 없는 상태에서도 미생물에 대해 선천적인 보호 기능을 제공합니다. 자가면역 질환에서는 대체 보체 경로가 조직 손상에 직접적으로 기여할 수 있습니다.
시험 시료에서 보체 인자 B 절단 생성물을 평가함으로써 샘플이 채취될 때 대체 경로가 얼마나 활성화되었는지를 추정할 수 있습니다. 당사의 ELISA 키트는 보체 인자 B 활성화를 정확하게 측정할 수 있는 간단하고 신속하며 비방사선적이고, 매우 특이적이고 정량적인 절차를 제공합니다. 이는 대체 보체 경로의 역할이나 상태를 여러 연구 및 임상 환경에서 조사하거나 Bb 생성의 모니터링을 위해 이상적입니다.
Sample
Serum, EDTA plasma
Species Reactivity
Human
Intended Use
DEIASL036 detects complement factor B activation fragment.
The ELISA kit measures the amount of the complement fragment Bb, an activation fragment of Factor B of the alternative pathway of complement, in human plasma or serum. Measurement of Bb in human plasma or serum provides evidence of the involvement of the alternative pathway of complement. Measurement of alternative pathway activation aids in the diagnosis of several kidney diseases, e.g., chronic glomerulonephritis, lupus nephritis, as well as several skin diseases, e.g., dermatitis herpetiformis and pemphigus vulgaris. Other diseases in which activation of the alternative pathway of complement has been observed include rheumatoid arthritis, sickle cell anemia, and gram-negative bacterial infections.
Storage
Store the unopened kit at 2°C to 8°C. After the kit is opened, the 20X Wash Solution Concentrate and Hydrating Reagent may be stored at 2°C to 25°C.
All reagents must be brought to room temperature (15°C to 25°C) before use. Place all unused microassay strips into the storage bag, reseal the bag, and store at 2°C to 8°C.
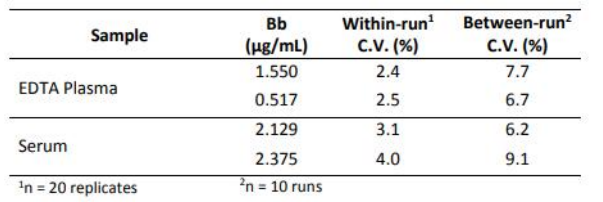
Precision
Within-run and between-run precision was determined by assaying 20 replicates of 2 plasma samples and 2 serum samples in 10 different runs.
Detection Limit
LOD: The limit of detection (LOD) for the Bb Plus EIA is 0.018 μg/mL, determined by the upper 3SD limit in a zero standard study.
LLOQ: The lower limit of quantitation (LLOQ) for the Bb Plus EIA is 0.033 μg/mL, the lowest concentration on the standard curve that met NCCLS criteria for accuracy and precision.
ULOQ: The upper limit of quantitation (ULOQ) for the Bb Plus EIA is 0.836 μg/mL, the highest concentration that met NCCLS criteria for accuracy and precision.
General Description
The alternative complement pathway provides innate protection against microbial agents in the absence of specific antibody. The activation of this complement pathway can be triggered by a variety of substances including microbial polysaccharides or lipids, gram-negative bacterial lipopolysaccharides, and surface determinants present on some viruses, parasites, virally infected mammalian cells, and cancer cells. In autoimmune diseases, the alternative complement pathway may contribute directly to tissue damage.
A centrally important reaction that occurs during alternative pathway activation is the conversion of the 93 Kd molecular weight Factor B zymogen to an active proteolytic enzyme. This is accomplished in a two-step reaction. During the first reaction step the Factor B forms a magnesium-dependent complex with C3(H20) or C3b. The C3(H20),B complex is formed only in fluid-phase while the C3b,B complex can be formed either in fluid-phase or on a target surface. Factor B, which is present in the C3(H20),B or the C3b,B complex, is cleaved into the Ba (33 Kd) and Bb (60 Kd) fragments in the second reaction step by the alternative pathway enzyme, Factor D.1-4 The resulting C3b,Bb bimolecular complex is the C3 convertase enzyme of the alternative pathway. The Bb subunit is the catalytically active site of the complex that is capable of cleaving C3 to C3a and C3b fragments. The additional C3b fragments produced in this manner may form the C3b,Bb,C3b rimolecular complex that is the C5 convertase enzyme of the alternative pathway. This C5 convertase is capable of cleaving C5 to C5a and C5b fragments.
The C3 and C5 convertases of the alternative pathway can be stabilized by Factor P (also called Properdin), a component of the alternative pathway normally present in human plasma or serum, or by C3 nephritic factor, an autoantibody produced in some patients experiencing extensive alternative pathway activation. The C3 and C5 convertases of the alternative pathway can be dissociated, and thereby inactivated, by spontaneous decay dissociation, or by the binding of Factor H or Complement Receptor 1 (CR1 ). The Bb fragment that is dissociated from either convertase retains some biological activities, e.g., retention of functional hemolytic activity, the ability to induce macrophage- spreading, and plasminogen activation.
Although alternative pathway activation is thought to occur primarily in the absence of specific antibody, many situations arise in which alternative pathway activation can occur as the result of classical pathway activation. For example, immune complexes that are present in autoimmune disease patients can trigger classical complement pathway activation with resultant production of C3b fragments. As described above, these C3b molecules are capable of binding Factor B and initiating its cleavage into the Ba and Bb fragments. Thus, alternative pathway activation can occur in antibody-mediated autoimmune disease states and may contribute significantly to enhanced complement activation and concomitant tissue destruction.
By assessing Factor B cleavage products in test specimens, one can estimate the extent of alternative pathway utilization occurring at the time of sample collection in the disease state under investigation. The ELISA Kit provides a simple, rapid, non-radioactive, highly specific, and quantitative procedure for measuring Factor B activation. It is ideal for investigations involving the role or status of the alternative complement pathway in numerous research and clinical settings, and for monitoring the generation of Bb in vitro.
Standard Curve
The standard curve for the Bb EIA is generated using the blank subtracted A450 values for each Standard (on the y axis) and the assigned concentration for each Bb Plus Standard (on the x axis). After linear regression, the generated standard curve must meet the validation requirements (see below). Most computers and calculators are capable of performing these calculations. Alternatively, the data may be graphed manually and the values (μg/mL) of the test samples read directly from the best-fit line of the standard curve. An example of a typical standard curve is shown in Figure 1.
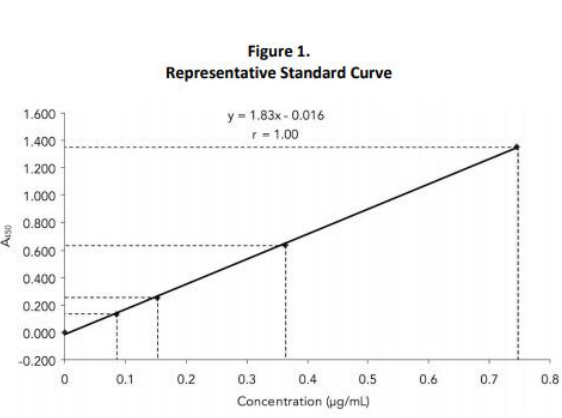 Determine the slope, intercept, and correlation coefficient of the derived best-fit line. The values must be within the specified ranges to qualify the assay:
Determine the slope, intercept, and correlation coefficient of the derived best-fit line. The values must be within the specified ranges to qualify the assay:  Refer to the vial labels or product C of A for the mean acceptable Bb concentration ranges for the High and Low Controls.
Refer to the vial labels or product C of A for the mean acceptable Bb concentration ranges for the High and Low Controls.
Citations
Have you cited DEIASL036 in a publication? Let us know and earn a reward for your research.
CD Creative Diagnostics의 모든 제품을 만나보세요!
Products
Self-Assembled Monolayers Reagents
Protein-Based Fluorescent Nanoparticles
CD Creative Diagnostics - Official Distributor in South Korea "Morebio" 한국 공식 대리점 "모아바이오"